Generate Ssh Key Putty And Use In Centos
- Generate Ssh Key Putty And Use In Centos Download
- Ssh On Centos
- Generate Ssh Key Putty And Use In Centos 1
SiteGround uses key-based authentication for SSH. This has proven more secure over standard username/password authentication. More information on SSH keys can be found here. You can generate an SSH key pair directly in cPanel, or you can generate the keys yourself and just upload the public one in cPanel to use with your hosting account. This guide describes how to generate and use a private/public key pair to log in to a remote system with SSH using PuTTY.PuTTY is an SSH client that is available for Windows and Linux (although it is more common on Windows systems). How to Generate SSH Keys on PuTTY. SSH keys are one of the most secure SSH authentication options. It is definitely more secure than the usual SSH password authentication. Therefore, it is highly recommended to use SSH Key authentication method for connections to your servers.
- Nov 26, 2017 This video shows how to log into a CentOs 7 server from a Windows machine using SSH keys. The video will show you how to generate the keys using Putty and then how to configure your CentOS.
- Jul 19, 2013 PuTTY Key Generator (a.k.a. PuTTYgen) While PuTTY is a client program for SSH (in addition to Telnet and Rlogin), it is not a port of or otherwise based on OpenSSH. Consequently, PuTTY does not have native support for reading OpenSSH's SSH-2 private key files. However, PuTTY does have a companion named PuTTYgen.
- PuTTY does not natively support the private key format for SSH keys. PuTTY provides a tool named PuTTYgen, which converts keys to the required format for PuTTY. You must convert your private key (.pem file) into this format (.ppk file) as follows in order to connect to your instance using PuTTY.
- Nov 10, 2011 How to Generate A Public/Private SSH Key Linux By Damien – Posted on Nov 10, 2011 Nov 18, 2011 in Linux If you are using SSH frequently to connect to a remote host, one of the way to secure the connection is to use a public/private SSH key so no password is transmitted over the network and it can prevent against brute force attack.
With a secure shell (SSH) key pair, you can create virtual machines (VMs) in Azure that use SSH keys for authentication, eliminating the need for passwords to sign in. This article shows you how to quickly generate and use an SSH public-private key file pair for Linux VMs. You can complete these steps with the Azure Cloud Shell, a macOS or Linux host, the Windows Subsystem for Linux, and other tools that support OpenSSH.
Note
VMs created using SSH keys are by default configured with passwords disabled, which greatly increases the difficulty of brute-force guessing attacks.
For more background and examples, see Detailed steps to create SSH key pairs.

Generate Ssh Key Putty And Use In Centos Download
For additional ways to generate and use SSH keys on a Windows computer, see How to use SSH keys with Windows on Azure.
Supported SSH key formats
Azure currently supports SSH protocol 2 (SSH-2) RSA public-private key pairs with a minimum length of 2048 bits. Other key formats such as ED25519 and ECDSA are not supported.
Create an SSH key pair
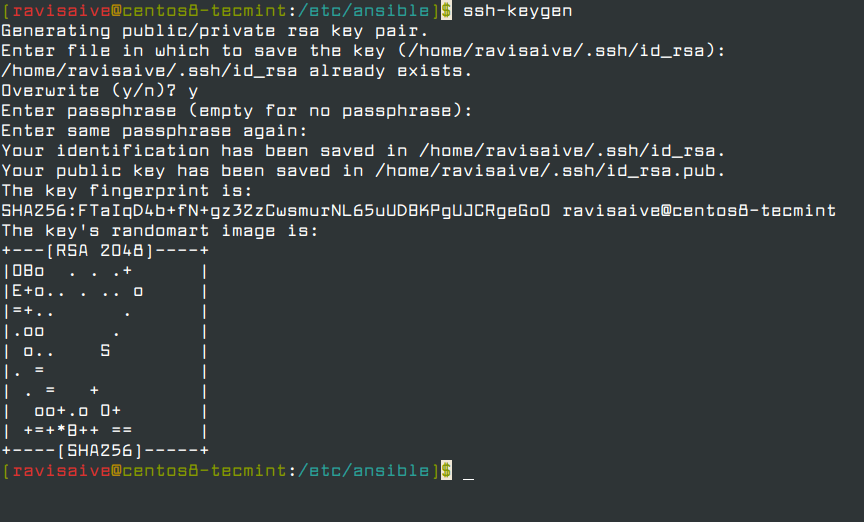
Use the ssh-keygen command to generate SSH public and private key files. By default, these files are created in the ~/.ssh directory. You can specify a different location, and an optional password (passphrase) to access the private key file. If an SSH key pair with the same name exists in the given location, those files are overwritten.
The following command creates an SSH key pair using RSA encryption and a bit length of 4096:
If you use the Azure CLI to create your VM with the az vm create command, you can optionally generate SSH public and private key files using the --generate-ssh-keys/windows-10-activation-key-generator-download-free.html. option. The key files are stored in the ~/.ssh directory unless specified otherwise with the --ssh-dest-key-path option. The --generate-ssh-keys option will not overwrite existing key files, instead returning an error. In the following command, replace VMname and RGname with your own values:
Provide an SSH public key when deploying a VM
To create a Linux VM that uses SSH keys for authentication, specify your SSH public key when creating the VM using the Azure portal, Azure CLI, Azure Resource Manager templates, or other methods:
If you're not familiar with the format of an SSH public key, you can display your public key with the following cat command, replacing ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub with the path and filename of your own public key file if needed:
A typical public key value looks like this example:
If you copy and paste the contents of the public key file to use in the Azure portal or a Resource Manager template, make sure you don't copy any trailing whitespace. To copy a public key in macOS, you can pipe the public key file to pbcopy. Similarly in Linux, you can pipe the public key file to programs such as xclip.
The public key that you place on your Linux VM in Azure is by default stored in ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub, unless you specified a different location when you created the key pair. To use the Azure CLI 2.0 to create your VM with an existing public key, specify the value and optionally the location of this public key using the az vm create command with the --ssh-key-values option. In the following command, replace VMname, RGname, and keyFile with your own values:
If you want to use multiple SSH keys with your VM, you can enter them in a space-separated list, like this --ssh-key-values sshkey-desktop.pub sshkey-laptop.pub.
SSH into your VM
With the public key deployed on your Azure VM, and the private key on your local system, SSH into your VM using the IP address or DNS name of your VM. In the following command, replace azureuser and myvm.westus.cloudapp.azure.com with the administrator user name and the fully qualified domain name (or IP address):
If you specified a passphrase when you created your key pair, enter that passphrase when prompted during the login process. The VM is added to your ~/.ssh/known_hosts file, and you won't be asked to connect again until either the public key on your Azure VM changes or the server name is removed from ~/.ssh/known_hosts.
If the VM is using the just-in-time access policy, you need to request access before you can connect to the VM. For more information about the just-in-time policy, see Manage virtual machine access using the just in time policy.
Ssh On Centos
Next steps
Generate Ssh Key Putty And Use In Centos 1
For more information on working with SSH key pairs, see Detailed steps to create and manage SSH key pairs.
If you have difficulties with SSH connections to Azure VMs, see Troubleshoot SSH connections to an Azure Linux VM.